SICM and SICM based SECM Applications for Live Cell Research

SICM and SICM based SECM Applications for Live Cell Research
Park Systems AFM Seminar and Live Demo
Le Forum des Microscopies à Sondes Locales 2019 / Marseille, France
When:
- - Tuesday, March 19, 9:00-12:00 / AFM School for Biological Application
- - Wednesday, March 20, 20:30 / Late Night AFM Workshop (after the conference dinner)
Presenter:
Sang-Joon Cho
VP of Park Systems and Director of R&D Center at Advanced Institute of Convergence Technology, SNU
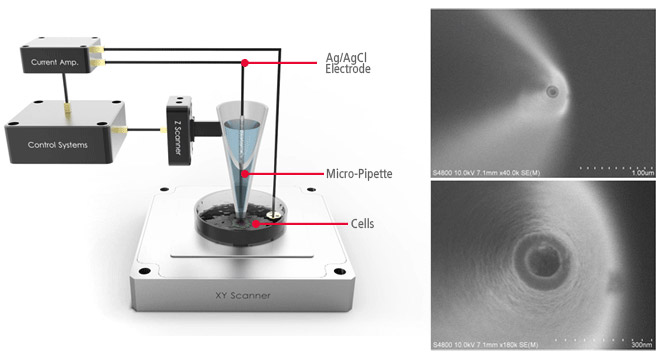
SICM with nanopipettes
ABSTRACT
The high-resolution monitoring of live cell membranes in physiological conditions has been the homework for centuries for biologists. Visualization and Understanding of cell membrane activities could give precious insight upon how cells interact with outer environment. Scanning ion conductance microscopy (SICM) can provide the surface morphology of biological soft materials in liquid directly. The SICM uses ionic current as feedback signal by detecting it through the nano-size opening of glass pipette. The dedicated SICM operating mode called approach and retract scanning (ARS) makes SICM imaging stable in liquid environment. The in-liquid imaging capability without physical contact allows using SICM for various cell study topics in live status such as cell division, fusion, and other fundamental physiological phenomena. For optimal performance, accurate control of the tip position is a critical issue. We present a novel closed-loop control strategy for the ARS mode that achieves higher operating speeds with increased stability. In addition to the obtaining morphology using SICM, minor modification of system and nano pipette could provide valuable information on redox activity of individual cells. Convenient distance control capability and high resolution 3D surface mapping of SICM could enhance the accuracy of SECM measurement. The presenting examples are one of many new possible applications and new challenges in the growing multi-disciplinary study of cell biology.
References
[1] G. E. Jung, H. Noh, Y. K. Shin, ... and S. J. Cho, Nanoscale 7(25) 10989 (2015).
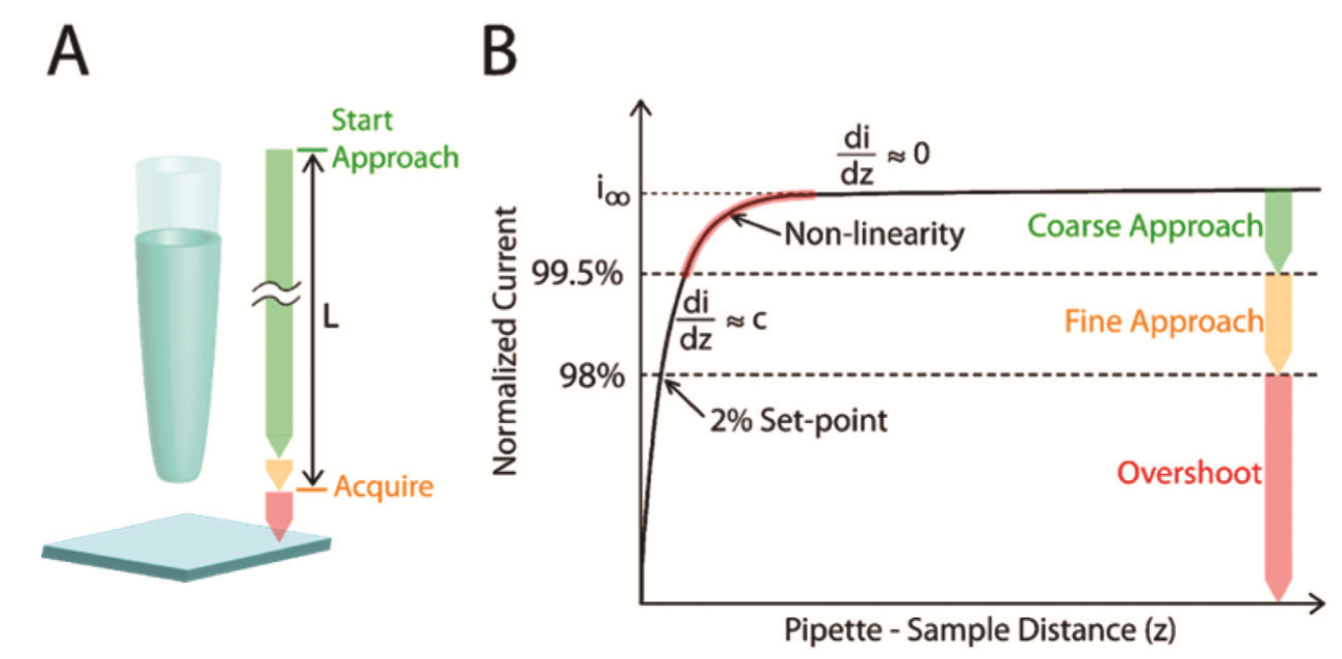
Fig. 1: Measurement strategy for the Closed Loop-ARS mode. (A) Schematic of the proposed CL-ARS algorithm. (B) Normalized ion current through pipette, i/i∞, as a function of pipette–surface distance, z.
Registration and contact: pse@parksystems.com | www.parksystems.com
